Home > Pathologies and treatments > Cataract
Cataract
What is it?
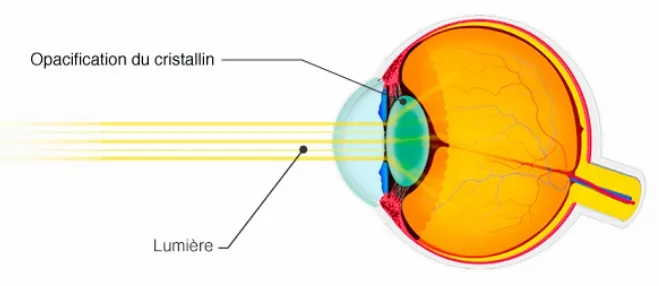
Cataract is an eye condition characterized by the progressive opacification of the lens, the natural lens of the eye. This opacity prevents light from passing properly through the eye, resulting in blurred, clouded or veiled vision.
Symptoms of cataract
• Blurry or blurred vision
• Feeling of seeing through a veil
• Increased sensitivity to light and glare
• Difficulty seeing at night
• Color change (yellowish tint)
• Frequent need to change glasses
The causes of cataracts
Cataract is primarily related to aging, but other factors may also be involved:
• Advanced age (primary cause)
• Excessive UV exposure without protection
• Smoking and alcoholism
• Diabetes (diabetic cataract)
• Eye trauma
• Heredity (genetic factors)
• Certain medications (including corticosteroids)
Treatment of cataract
The only effective treatment is surgery. The procedure involves replacing the clouded lens with an artificial intraocular implant. The operation is fast (15-30 min), painless and generally very effective.
The choice of intraocular implant (or intraocular lens, IOL) after cataract surgery depends on several factors including lifestyle, vision needs and patient expectations. The main types of implants available are:
Which implant to choose ?
1. Monofocal implant (most common)
✅ Benefits:
Provides good vision from far or near (but not both).
Less halos and night glare.
Covered by social security and mutual funds.
❌ Cons:
Requirement to wear close vision glasses if the implant is set for long-range vision, and vice versa.
🔹 For whom? Patients who want clear vision at a single distance and agree to wear glasses.
2. Multifocal implant (corrects vision from far and near)
✅ Benefits:
Allows to see at several distances without glasses (or with less dependence).
Ideal for people who want more visual autonomy.
❌ Cons:
May cause halos of light at night and a slight decrease in contrast.
Less well tolerated in some patients.
Higher cost, often not reimbursed by social security.
🔹 For whom? Active patients who want to do without glasses in most situations.
3. Extended Depth of Field (EDOF) implant
✅ Benefits:
Good long and intermediate vision (computer, dashboard).
Less halos than multifocal implants.
Good alternative for those who do not tolerate multifocal implants.
❌ Cons:
Close-up vision is sometimes less clear than with a multifocal implant.
Higher cost.
🔹 For who?
Those who work on computers and want to reduce their addiction to glasses.
4. Toric implant (corrects astigmatism)
✅ Benefits:
Corrects astigmatism in addition to cataract.
Can be combined with a monofocal or multifocal implant.
❌ Cons:
More expensive and often not refunded.
🔹 For who? Astigmatic patients who want clearer vision without glasses.
How to choose ?
The choice is made with the ophthalmologist according to:
🔹 Your lifestyle (need to see without glasses, driving at night, working on screen, etc.).
🔹 Your tolerance to side effects (halos, contrast decrease).
🔹 Your budget, as some implants are not supported.
Result
✔️ Sharper and brighter vision: the lens opacity is removed.
✔️ Better color perception: colors become more vivid and natural.
✔️ Reduction of addiction to glasses (depending on the chosen implant).
✔️ Rapid recovery: vision usually improves in a few days.
